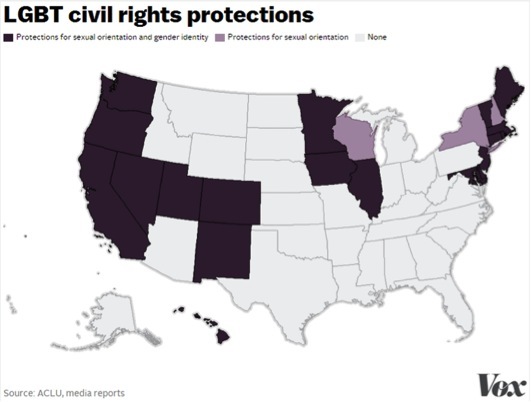
Indiana's new anti-LGBT law is so offensive it may cause talented young workers who drive economic growth to flee the state for more welcoming, diverse environments. Other states are similarly hostile to LGBT Americans; even without overt discriminatory laws like Indiana's, it remains legal in 29 states for a business owner to deny service to a gay person based on his or her sexual orientation. In 15 states, same-sex marriage is still constitutionally barred. But Indiana's new law is just one example of the many elements forcing talented people out of certain states and into more appealing ones. In coming years, this dynamic may result in a sharp divergence between progressive states with robust economies and conservative states mired in economic stagnation.
Americans' increasing mobility in recent decades has resulted in demographic sorting in which cities, states, and regions are now more politically segregated than ever. While swelling polarization has meant unprecedented gridlock in our nation's capital, the upshot across the states is a set of policy experiments that may yield decidedly different outcomes. Democrats and Republicans have elected leaders with vastly different values in key areas like diversity and inclusion, the minimum wage, and government investment in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and R&D. As these states implement their policy preferences, those choices drive migration into and out of certain states. In an age of rapid technological advancement and globalization, economic growth in the "knowledge economy" of the 21st Century is powered by innovation and ideas more than old-school manufacturing and elbow grease. Creative people who generate these ideas, therefore, are the linchpin of a dynamic, modern economy.
Aside from oil-rich states, already the economies of progressive states with cities that attract energetic, creative people like Seattle, San Francisco, New York, Boston, Chicago, and Minneapolis are leading the way. Mobile and talented Millennials who continue to leave dusty conservative states for greener, more progressive pastures will likely accelerate economic growth in their adopted states. Meanwhile, the dumb states--those that devalue education, deny science, promote bigotry, and refuse, out of sheer political spite, to accept federal funding for healthcare--are destined to wallow in a self-induced "brain drain death spiral."
The national reaction to the anti-gay "religious freedom" bill Indiana Gov. Mike Pence (R) signed on March 26th was swift and definitive. Although Jeb Bush and every GOP presidential contender heaped praise on Indiana's discriminatory law, business leaders voiced strong opposition. Apple CEO Tim Cook took to the Washington Post to condemn the "dangerous" new law. Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff quickly cancelled all employee travel to Indiana, and Angie's List, headquartered in Indianapolis, scrapped a $40 million expansion in response to the law. In all, CEOs of nine major corporations based in Indiana called on Pence to change the law, and last week, Pence signed a nominal "fix" to the statute, which seemingly pleased no one.
Seattle billionaire venture capitalist Nick Hanauer wasted no time laying into Pence. In a series of tweets, Hanauer underscored the economic folly of manifestly enshrining into law discrimination against LGBT citizens. "Growth in technological economies is all about innovation," he wrote. "The more innovation, the faster living standards improve." Hanauer explained that diversity is at the core of the evolutionary process of innovation, "super-charging" growth in technological economies. Inclusion is key to growth, and pluralistic cities tend to clobber monocultures like Indiana in the competitive marketplace. Furthermore, he noted, LGBT people are "uncommonly creative, and innovative," and invigorate the most dynamic and successful companies.
As states like Indiana devolve into "economic backwaters," Hanauer predicts, not only will LGBT workers flee, so will other smart people who appreciate that diversity is the key to innovation and growth. What is left behind is a "homogenized, narrow, and increasingly prejudiced population, who elect the same kind of leaders." These leaders enact laws that chase away more smart, diverse people, resulting in what Hanauer calls a "brain drain death spiral." The economy is consigned to a stagnant swamp or, at best, a "low wage competitor to Bangladesh." But Hanauer says the world faces tremendous challenges, and we need talented citizens to confront them. Therefore, his message to these people is simple: "Come to places like Seattle that will embrace you, and leverage your talents. We need you. The world needs you. Indiana, apparently, does not."
Years ago, Hanauer decided to leave the insulated world of the super-rich after realizing that discredited trickle-down economic policies were destroying his customer base. He has become a writer and political activist, advancing what he and colleague Eric Liu call "middle-out" economics. This "long-overdue rebuttal" to trickle-down theory states a simple, fundamental law of capitalism: If workers have more money, businesses have more customers. Thus, middle-class consumers are the true job creators, not rich businesspeople, and "a thriving middle class is the source of American prosperity, not a consequence of it."
One year ago, I delivered a similar message in a speech to the Downtown Rotary Club in my native hometown of Sioux Falls, SD. Not surprisingly, it wasn't well received. The members of this club--most of them old and male, and all of them white--represent the social and economic elite of Sioux Falls. I mentioned Charles de Gaulle's grim observation--"The cemeteries of the world are full of indispensable men"--and explained that the next 30 years in America will look very different than the last 30. The best way to maximize the prospects for economic growth in coming decades is to make the community more hospitable for talented Millennials. Change can be uncomfortable, I acknowledged, but future growth will depend largely on how much the community values diversity of ethnicity, gender, political opinions, sexual orientation, and religious beliefs (or lack thereof).
ECONOMIC GROWTH AND THE ROLE OF HUMAN CAPITAL
Economic growth is something everyone supports, but few stop to think about what it actually is. In his excellent book, "Here's the Deal," David Leonhardt sums it up succinctly. Over time, he writes, societies learn how to perform certain tasks, like growing food or transporting goods, more efficiently. What's more--some people even figure out how to perform entirely new tasks, like building skyscrapers, treating diseases that once wiped out entire civilizations, and communicating across great distances. People live better, and they live longer. In the simplest terms, that is economic growth.
Throughout America's history, our periods of greatest economic expansion have been precipitated by prudent investments in infrastructure and education, and a healthy influx of diverse, immigrant populations. Both private and public investment fueled growth, as with the Erie Canal, the transcontinental railroad, and the interstate highway system. The initial GI Bill educated America's World War II veterans and helped power the postwar boom that created the largest middle class the world has ever known. In response to Sputnik and the Soviet challenge, we redoubled our efforts in 1958 with the National Defense Education Act. This renewed focus on scientific research not only enabled America's victory in the Space Race, it also led to development of the jet engine for commercial aviation, the discovery of critical vaccines, and the early foundation for the Internet. Defense R&D spending also enabled other essential technologies to blossom, such as microwave ovens, digital cameras, and GPS.
Today's spending on education and R&D, in areas like micro-, nano-, and biotechnology, will plant the seeds for tomorrow's economic growth. But supply-siders in America who believe in cutting these investments in favor of tax breaks for the super-rich put all of that at risk. As Hanauer puts it, giving additional tax breaks to the richest 1% to encourage private investment is like trying to add water to the ocean to make it more wet. Already, he points out, American companies funnel huge portions of their profits into gimmicks that impress stock analysts in the short term but do nothing to add company value in the long run. He notes:
Over the past decade, the companies that make up the S&P 500 have spent an astounding 54 percent of profits on stock buybacks. Last year alone, U.S. corporations spent about $700 billion, or roughly 4 percent of GDP, to prop up their share prices by repurchasing their own stock.
There is, of course, a better way to invest in our future.
In the global economy, we usually think of 'capital' as the physical goods and materials that drive production, like buildings, equipment, raw materials and manufactured goods. Control of capital is the primary means of creating wealth. But in recent decades, especially as we have entered into a new stage in global economic development known as the "knowledge economy," it has become ever more important to focus on human capital.
Human capital refers to people's abilities, knowledge, and skills, and it explains why education is the lifeblood of economic growth. Education and training enable people to produce more valuable goods more efficiently. These improvements in production, in turn, allow companies to manufacture sophisticated products and provide premium services with worldwide demand, creating high-wage jobs as a result. All other economic investments--from infrastructure and transportation to medicine and alternative energy--can be leveraged through education and advancement of human capital.
Along with employers and their workers in the private sector, governments invest in human capital by way of education and training. Around the world we're seeing how countries that invest most actively in knowledge creation and innovation (through R&D), along with knowledge dissemination (through investments in education, training, and IT) are enjoying faster, sustainable economic growth. Countries that have stopped spending on these investments, by contrast, have seen their economies stall.
Leonhardt chronicles how the federal government has tracked its non-military spending on research, education, and training since 1962. From the 1960s into the early 1980s, the level of investment spending remained steady from year to year, and although it was still relatively small--less than 3 percent of GDP--it was crucial to U.S. economic growth over this period. The same culture of innovation in science and technology that lifted America into Space and to the surface of the moon also ignited the entrepreneurial engine of American economic growth. In the 1980s, however, R&D spending slipped by more than a third, and has never recovered.
THE IMPORTANCE OF CIVIC LEADERSHIP
Like Indiana, South Dakota suffers from a lack of civic leadership among its political and business elites. If leaders who value diversity and support investments in human capital are required to achieve sustainable, economic growth, South Dakota risks falling further behind more progressive states. In 2014, Democrats were successful in referring a statewide ballot initiative for a modest $1.25 increase in the minimum wage--from $7.25 to $8.50 per hour. If the minimum wage had kept pace with inflation alone, it would be well over $10 already. And if it were actually keeping pace with increases in workers' productivity--which has doubled in the past 40 years--it'd be over $21 per hour. Recalling how economic growth is the result of increases in productivity, we can easily see how almost all of those extra profits are flowing to CEOs and shareholders, and not at all to many of the workers performing the labor.
The South Dakota Chamber of Commerce opposed the meager minimum wage increase, citing concerns about job losses. Never mind that a 2009 meta-analysis of 64 different studies found little or no evidence of a negative association between minimum wages and employment. Moreover, raising the minimum wage actually boosts overall economic activity by increasing consumer demand. Lower-wage workers are much more likely to spend their extra earnings, pumping that money back into the economy, which fuels growth.
In 1914, Henry Ford shocked the entire business world by unilaterally doubling the wages of his thousands of production workers to $5 per day. Ford was no bleeding-heart liberal. Rather, in recognizing that the automobile would be more successful as a volume business than as a niche product for the mega rich--especially at a time before the U.S. had much of a consumer credit industry--Ford built a Model T car his own employees could buy. The Wall Street Journal and other business observers predicted doom and gloom--that Ford's unprecedented move would destroy American capitalism. But they were wrong. Within two years, profits doubled, and sales continued to boom. By 1921, Ford had half the U.S. car market. Ford would later say that the raise in wages was one of the finest business investments he ever made.
Washington State teaches a more recent lesson on wages and economic growth. In 1998, Washington residents voted to raise the minimum wage and link it to the cost of living. Of course, opponents at the time warned that the measure would be a job killer. But over the last 15 years, as the state's minimum wage climbed to $9.32--the highest in the country--job growth in Washington has out-paced the national rate, while poverty has trailed the U.S. level for at least 7 years. Seattle and the State of Washington are a sponge for educated professionals and the highly talented creative class. Many of these people are Millennials; many of them are LGBT; almost all are allies. Embracing LGBT Americans and their friends is just one of many lessons Indiana, South Dakota, and other states should learn from high-growth, forward-thinking cities and states. Increasing workers' wages is another.
In 2013, Hanauer made "The Capitalist's Case for a $15 Minimum Wage." Like critics of Ford's historic wage increase, Tim Worstall of Forbes labeled the proposal "insane." Less than a year later, the city of Seattle passed a $15 minimum wage, which is being implemented now. In a recent poll, 74 percent of Seattle voters supported the new law.
The marketplace seems to support Seattle's higher wages, too. Over the next two years, Seattle will increase its minimum wage incrementally, reaching $15 by 2017. Last week it was increased to $11 per hour; before that, it was already nearly 30 percent higher than the federal minimum wage. This hasn't exactly crippled the local economy. In fact, America's two cities with the highest rate of job growth by small businesses are Seattle and San Francisco, the two cities with the highest minimum wages. Seattle is the fastest-growing big city in the nation. As Hanauer puts it, "Fifteen dollars isn't a risky, untried policy for us. It's doubling down on the strategy that's already allowing our city to kick your city's ass."
South Dakota's stingy approach to education is perhaps its greatest shame. As a candidate for governor in 2010, Republican Dennis Daugaard ran glossy TV ads showing him sitting in a science lab, talking about education. At the time, South Dakota was dead last in the nation in teacher pay. Today, the state remains dead last, right behind Mississippi. Teachers are leaving because they can't make a living. In its 2014 annual study on the best and worst state public education systems in America, Education Week listed South Dakota as one of the 10 worst. The state earned a D or worse in 4 of the 6 categories reviewed. Yet Republicans' political monopoly in South Dakota perpetuates this failed approach. Daugaard, a back-bencher in the state legislature before he was plucked from obscurity in 2002 to serve as lieutenant governor, was re-elected last year with more than 70% of the vote. But how many talented, creative young teachers want to remain in a state that seems content to trail even Mississippi in teacher pay? Moreover, how many innovative Millennials want to work and raise their kids in a state where top officials reject the science of climate change and question the teaching of evolution?
A third lesson involves healthcare. The great moral scandal in policymaking of our time is the refusal by some Republican-controlled states to expand Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. On this issue, South Dakota is worse than Indiana, where even Gov. Pence has agreed to a deal with the Obama Administration to expand Medicaid, albeit with a watered-down plan that insures far fewer Hoosiers. Gov. Daugaard, on the other hand, refuses to budge, arguing that "able-bodied adults" do not deserve assistance for healthcare, even when accepting that assistance would provide an economic boon to the state. If South Dakota expanded its Medicaid program, it would be responsible for about $5.3 million in administrative costs over the first three years. In return, the federal government would supply $654 million to help cover approximately 49,000 low-income South Dakotans.
On the Medicaid issue, leadership in South Dakota has been abysmal. Politicians have stubbornly refused to accept the federal funding, and top business officials have been indifferent or powerless. Two gigantic hospital systems drive the Sioux Falls economy and although their advocates wholeheartedly support expansion, they have been unable to convince the city's chamber of commerce to begin studying the issue. A recent analysis commissioned by the South Dakota Association of Healthcare Organizations, however, estimated that the state treasury would see a net surplus of $63 million in revenue over the next seven years under Medicaid expansion, even after the state had paid its nominal share of expenses. Even more compelling is the overall economic benefit of expansion for South Dakota, estimated at a whopping $1.04 billion over this time period. Researchers in other states have also found that expanding Medicaid will improve state budget outlooks, spur job creation, and reduce taxpayer costs associated with uninsured patients.
Contrast South Dakota's lackadaisical and know-nothing approach to public policy with that of Gov. John Kasich, who bucked his own party in the state legislature to expand Medicaid in Ohio. In this case, the Ohio Chamber of Commerce actively lobbied Kasich, a respected conservative Republican and former budget hawk in Congress. In addition, the Ohio Conference of Catholic Bishops wrote an open letter to the governor imploring expansion.
But in South Dakota, Bishop Paul J. Swain of the Catholic Diocese of Sioux Falls has refused to support expanding the program that provides life-saving care for the sick and the poor. The U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops affirms that "health care is a basic right flowing from the sanctity of human life," and dozens of bishops have publicly urged their states' governors to expand Medicaid. In a sharply worded editorial last year, for example, Bishop John C. Wester of Salt Lake City wrote, "Utah cannot proclaim itself a pro-life state so long as it refuses to provide access to basic health care coverage" by expanding Medicaid. Yet Swain--who before he joined the Catholic Church at age 40 was a policy advisor to Republican Gov. Lee Sherman Dreyfus of Wisconsin--has offered concerns about birth control as an excuse to remain on the sidelines.
VALUING DIVERSITY AND CHOOSING GROWTH
In 1932, U.S. Supreme Court Justice Louis Brandeis famously wrote in a dissenting opinion, "It is one of the happy incidents of the federal system that a single courageous state may, if its citizens choose, serve as a laboratory; and try novel social and economic experiments without risk to the rest of the country." Practically speaking, this dynamic isn't completely accurate today, since federal taxpayers regularly pick up the slack for the poorest states. South Dakota, for instance, receives more than two dollars in return for every dollar South Dakotans send to Washington in per capita federal taxes. Indiana taxpayers also come out ahead, on average. Red state politicians decry the "tyranny of big government," but without federal money to prop up local economies via spending on agricultural subsidies, roads and bridges, healthcare, military bases, and national parks, it is quite likely their states would lag even farther behind the smart ones.
But two major phenomena in recent years--growing political segregation, and the dynamism of the new global economy--might mean that progressive states that attract and invest in talented young people will flourish, while states clinging to the tired, disproven dogma of the past will flounder. Like many of the small, dilapidated towns that dot rural America, states like Indiana and South Dakota may indeed find themselves in a demographic death spiral. Granted, some states enjoy certain natural advantages over other states, like a favorable climate, access to waterways, and scenic beauty. But all states have the power to choose a growth-oriented approach upon which their future depends. The choice is theirs.