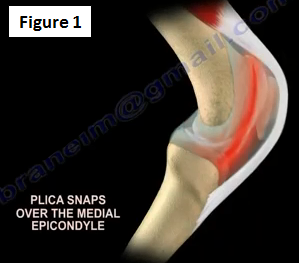
A painful knee plica is rare and it is a diagnosis of exclusion. The majority of knee plica is medial (Figure 1).
What is a knee plica?
It is an embryological remnant of the synovial folds (Figure 2). The synovial fold can become thickened and sometimes inflamed. It occurs in about 50% of patients and is due to a blunt trauma to the knee.
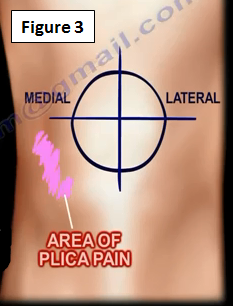
The knee plica can be suprapatellar or intrapatellar, but it is mostly medial (Figure 3). It is located over the medial femoral condyle and is vulnerable to trauma when the knee is flexed.
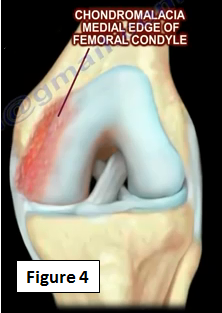
Repeated trauma or irritation may lead to inflammation and fibrosis of the plica. When fibrosis occurs in the plica, this decreases the elasticity and causes impingement on either the patella or the medial femoral condyle. Synovitis or chondromalacia may occur on the leading edge of the medial femoral condyle (Figure 4).
Evaluation of the Plica
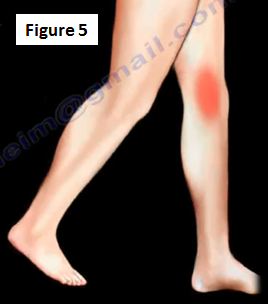
The diagnosis is usually done by exclusion. There is usually an activity related anteromedial or medial knee pain. There may be some catching of "giving way" of the knee. The patient may feel a snapping sensation or pain with repeated activity (Figure 5).
You may sometimes feel this band is tissue that is the medial plica (may role it under the finger). This band of tissue is sometimes painful. The presence of plica does not mean that it will make pathology or create symptoms.
How do you locate this plica?
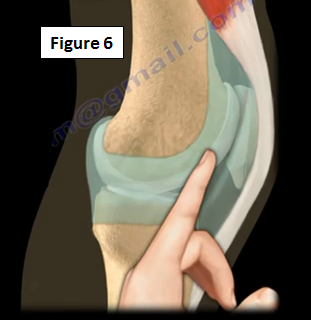
The plica can be palpated just above the joint line. The palpation is facilitated by having the patient flex and extend the knee while the physician palpates the medial femoral condyle next to the patella (Figure 6). An MRI of the knee might not detect the plica.
Treatment
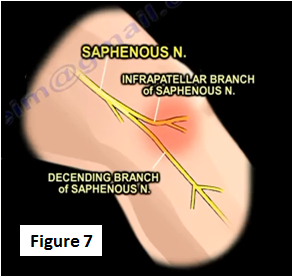
If the plica is symptomatic is can be treated by rest, NSAIDs, activity modification, physical therapy modalities (ultrasound or iontophoresis), or steroid injections. If these treatment methods fail, then resection of the plica could be done (it is rarely done, but is very effective). The physician should make sure to check for saphenous neuritis as a differential diagnosis (Figure 7).
For more information on the knee and knee injuries, follow the links below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c3643PM0a2o
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t0_U52KWkxY
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PCRkXW57Qhs
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SnfEmezg7eY
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_hYhdO5SqD4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QviesmjU8Q0
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1BS6JZlukfY
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UJB4eh-Vtz8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G9MPgxiZnoc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NzKaN99YdLQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k6Cdz7RxceQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CZ18PGwUG-0
For more information, visit my YouTube Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/user/nabilebraheim