A continuation of the intense drought in the southern Plains, wet and cool weather in the Pacific Northwest, and the potential for more temperature extremes were some of the highlights of the just-released official National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) winter forecast.
One of the major contributing factors to the forecast is the expected continuation and intensification of La Nina, which was noted in NOAA's preliminary winter forecast a couple of months ago and was also highlighted in the winter forecasts of other outlets.
The specific forecast details for December through February include the likelihood of:
- Colder- and stormier-than-average conditions in the northern Plains, a combination that would lead to the potential for heavy snow and the possibility of spring river flooding
The seemingly non-committal forecast for the Northeast and mid-Atlantic region, according to NOAA, was made because of other factors, such as the presence of the Arctic Oscillation, which can usually only be pinpointed a week or two in advance and trump any influences of La Nina.
A negative phase of the oscillation typically results in extreme cold in the Midwest, Northeast, mid-Atlantic region, and even the Deep South. This has occurred at times during each of the past two winters, and if it happens again this winter, it would mean more extreme cold and intense snow storms, especially in the Midwest and Northeast.
NOAA calls the Arctic Oscillation the "wild card" of the winter forecast, and it will ultimately have a tremendous effect on the weather for millions of Americans.
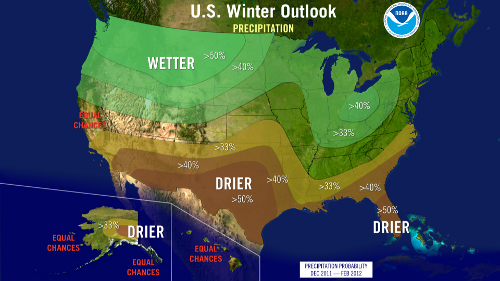
NOAA's seasonal forecast does not include specific predictions related to the amount of snowfall. The forecast highlights the areas where precipitation (rain, snow, and ice) are expected to be greater or less than average for that region. It also highlights areas where there are equal chances of above or below average precipitation.
The temperature forecast highlights areas where seasonal temperatures are expected to be above or below average, along with areas having equal chances of either.