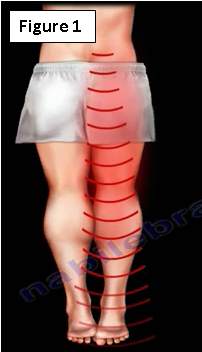
Acute low back pain or low back pain with sciatica radiating to the lower leg and to the foot (Figure 1). They are initially treated conservatively for at least six weeks by physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medication and limited activity (as guided by the pain).
Doctors should treat the condition conservatively. Even if there is a large disc herniation on the MRI, unless the disc is central or causing a neurological deficit, they need wait at least six weeks before beginning a more aggressive treatment. 90% of patients will have symptoms that resolve in one month. Smoking, depression and vibrations will increase the incidence of low back pain (Figure 2).
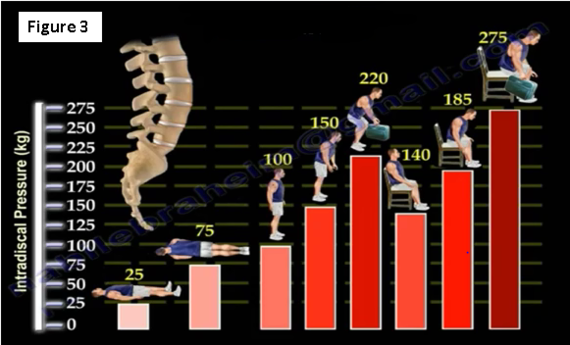
Intradiscal pressure (IDP) will change depending on the position (Figure 3). The lowest pressure is measured while the patient is lying supine. The highest IDP is measured while the patient is sitting, leaning forward and holding weight.
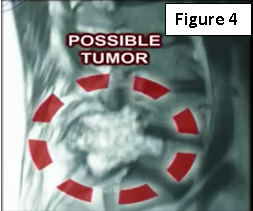
If the patient is experiencing low back pain and there is a history of cancer, the doctor will need to get an x-ray and MRI, especially if the pain occurs during rest and at night (Figure 4)! In case of a renal tumor, the physician will probably need to do arteriography and embolization of the spinal lesion.
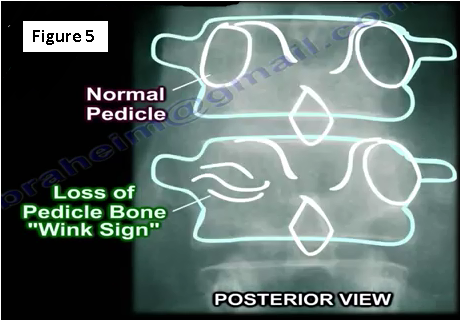
The spine is a common location for metastatic tumors. Metastases occur in the vertebral body and go to the pedicle. Loss of about 30%-40% of the bone mass must occur before the physician can detect the lesion on an x-ray. The loss of the pedicle bone will result in a "wink sign" (Figure 5).
What if the patient has an infection?
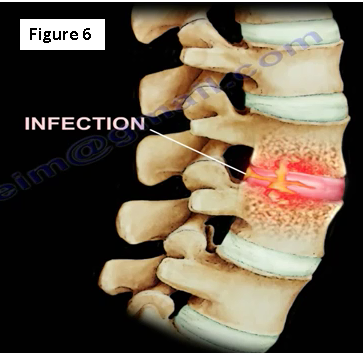
An infection will occur within the intervertebral disc space (Figure 6). The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels will be elevated. Only 50% of the cases will have a fever, and less than 50% of cases will have an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count. The physician will need to get a blood culture (this is positive in about 24% of the cases). They will also need to get an MRI and administer antibiotics as guided by the biopsy, culture and sensitivity.
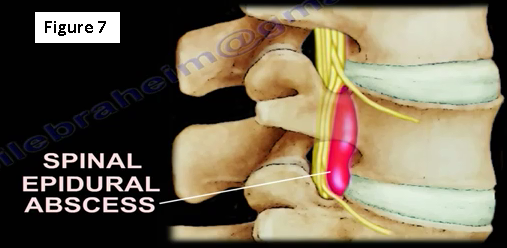
If the patient has an epidural abscess, surgery will be performed, especially if there is deterioration of the neurological function (Figure 7). If there is an infection post-surgery, it may be diagnosed with a higher C-reactive protein (CRP).
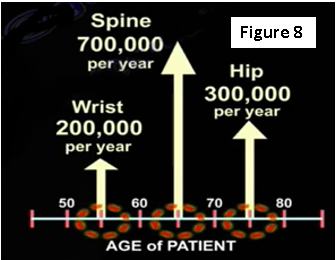
Osteoporotic bone is at risk of fracture, beginning with the wrist, the spine and followed by the hip (Figure 8). So, if the patient has an osteoporotic spine, it will need to be treated before it leads to a hip fracture later on. One fracture of the spine will lead to multiple spine fractures. After one year of treatment with medication, the incidence of a vertebral fracture is decreased by 60%. After two years, the incidence of a vertebral fracture is decreased by 40%.
In general, when the patient has low back pain, it is necessary to treat the patient conservatively. The doctor does not need to get x-rays in the first 4-6 weeks unless there are "red flags" including: the patient is older, the patient has a metastatic tumor or history of cancer, infection is suspected, the patient has trauma or there is an osteoporotic fracture possibly due to steroid use.
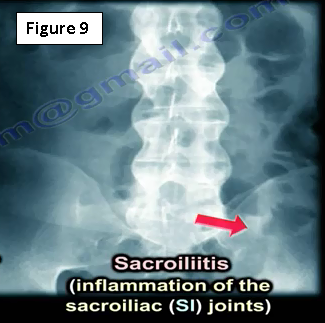
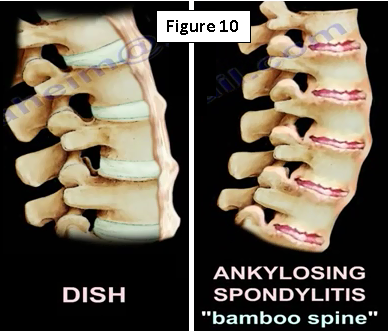
The physician may see an x-ray that looks like ankylosing spondylitis (Figure 9). They will need to check the SI joint because ankylosing spondylitis begins at the SI joint. The may get HLA-B27 and will find that there are marginal syndesmophytes with diffuse ossification of the disc space without large osteophyte formation. Ankylosing spondylitis is different from Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH), which occurs in diabetics, in this case the physician will get an HbA1c. Syndesmophytes are non-marginal and have larger osteophytes. It is the DISH which will have flowing ossification along the anterolateral aspect of at least four continuous vertebra. DISH is not ankylosing spondylitis (Figure 10)!
An MRI of the spine will be obtained at a certain point, however, x-rays may be needed first. MRI results may be a problem! There are abnormal MRIs in asymptomatic patients (these are false positives). Approximately 35% of these false positives are seen in patients less than 40 years of age. 90% of positive MRIs in asymptomatic patients occur in patients over 60 years of age.
The second issue is the MRIs with gadolinium dye. Gadolinium will differentiate a disc from a scar. Both granulation tissue and the recurrent disc could look alike on a routine MRI. There will be contrast enhancement when there is granulation tissue because it is vascular. However, when there is a disc herniation, the dye will not enhance because the disc is a dead piece of tissue (avascular). When the doctor tries to differentiate between a recurrent disc and a scar, they will inject the dye and get the MRI. If there is a vascular enhancement, then it is granulation tissue and the patient will not need surgical intervention. If there is no enhancement, then it is a recurrent disc and it is avascular, which is why it does not enhance. If the recurrent disc is causing a lot of pain or symptoms to the patient, then the physician may need to discuss a repeated surgery with this patient.
For more information on low back pain, visit the links below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DRG6018Kh1w
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0bby9NQ7Ln4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zfWKcTixM6E
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AWR1M90NG5s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PMQbe4tSp4g
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Myo7DrPWAM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kvxZH7wGDfc
For more information, visit my YouTube Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/user/nabilebraheim